Temperature sensor DS1820 / 22 is a sensor used to read the temperature value of an environment. Results DS1820 / 22 sensor readings will be in though by Arduino UNO with one wire interface. The sensor is capable of reading temperatures ranging from 0 ° C - 100 ° C and then the results are displayed on 2x16 LCD.
Hardware Requirement
- Arduino Uno Board
- DS1820/1822 Temperature Sensor
- LCD 16*2
- Power supply +5 Volt
- Jumper
DS1820 Temperature Sensor (Waterproof) | Source
Block Diagram
Schematic
Arduino - LCD Wiring
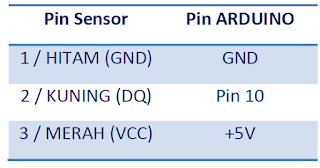
Arduini - DS1820 Wiring
Source Code/Sketch
#include <OneWire.h>
#include <Wire.h>
#include <LiquidCrystal.h>
LiquidCrystal lcd(2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7);
OneWire ds(10); // on pin 8 --DS1820
unsigned int temp;
//============================================
void setup(void) {
lcd.begin(16, 2);
lcd.print("Dig Term DS1820");
lcd.setCursor(0,1);
delay(1000);
}
//===========================================
void loop(void) {
byte i;
byte present = 0;
byte type_s;
byte data[12];
byte addr[8];
float celsius, fahrenheit;
//===================================
if ( !ds.search(addr)) {
ds.reset_search();
delay(250);
return;
}
// the first ROM byte indicates which chip
switch (addr[0]) {
case 0x10: // Chip = DS18S20 or old DS1820
type_s = 1;
break;
case 0x28: // Chip = DS18B20
type_s = 0;
break;
case 0x22: // Chip = DS1822
type_s = 0;
break;
default: //Device is not a DS18x20 family device.
return;
}
ds.reset();
ds.select(addr);
ds.write(0x44, 1); // start conversion, with parasite power on at the end
delay(1000); // maybe 750ms is enough, maybe not
// we might do a ds.depower() here, but the reset will take care of it.
present = ds.reset();
ds.select(addr);
ds.write(0xBE); // Read Scratchpad
for ( i = 0; i < 9; i++) { // we need 9 bytes
data[i] = ds.read();
}
int16_t raw = (data[1] << 8) | data[0];
if (type_s) {
raw = raw << 3; // 9 bit resolution default
if (data[7] == 0x10) {
raw = (raw & 0xFFF0) + 12 - data[6];
}
}
else {
byte cfg = (data[4] & 0x60);
if (cfg == 0x00) raw = raw & ~7; // 9 bit resolution, 93.75 ms
else if (cfg == 0x20) raw = raw & ~3; // 10 bit res, 187.5 ms
else if (cfg == 0x40) raw = raw & ~1; // 11 bit res, 375 ms
}
celsius = (float)raw / 16.0;
fahrenheit = celsius * 1.8 + 32.0;
temp=celsius;
//====================
lcd.setCursor(0,1);
lcd.print("Temp:");
lcd.print(temp);
lcd.write(0xDF);
lcd.print("C ");
}
#include <Wire.h>
#include <LiquidCrystal.h>
LiquidCrystal lcd(2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7);
OneWire ds(10); // on pin 8 --DS1820
unsigned int temp;
//============================================
void setup(void) {
lcd.begin(16, 2);
lcd.print("Dig Term DS1820");
lcd.setCursor(0,1);
delay(1000);
}
//===========================================
void loop(void) {
byte i;
byte present = 0;
byte type_s;
byte data[12];
byte addr[8];
float celsius, fahrenheit;
//===================================
if ( !ds.search(addr)) {
ds.reset_search();
delay(250);
return;
}
// the first ROM byte indicates which chip
switch (addr[0]) {
case 0x10: // Chip = DS18S20 or old DS1820
type_s = 1;
break;
case 0x28: // Chip = DS18B20
type_s = 0;
break;
case 0x22: // Chip = DS1822
type_s = 0;
break;
default: //Device is not a DS18x20 family device.
return;
}
ds.reset();
ds.select(addr);
ds.write(0x44, 1); // start conversion, with parasite power on at the end
delay(1000); // maybe 750ms is enough, maybe not
// we might do a ds.depower() here, but the reset will take care of it.
present = ds.reset();
ds.select(addr);
ds.write(0xBE); // Read Scratchpad
for ( i = 0; i < 9; i++) { // we need 9 bytes
data[i] = ds.read();
}
int16_t raw = (data[1] << 8) | data[0];
if (type_s) {
raw = raw << 3; // 9 bit resolution default
if (data[7] == 0x10) {
raw = (raw & 0xFFF0) + 12 - data[6];
}
}
else {
byte cfg = (data[4] & 0x60);
if (cfg == 0x00) raw = raw & ~7; // 9 bit resolution, 93.75 ms
else if (cfg == 0x20) raw = raw & ~3; // 10 bit res, 187.5 ms
else if (cfg == 0x40) raw = raw & ~1; // 11 bit res, 375 ms
}
celsius = (float)raw / 16.0;
fahrenheit = celsius * 1.8 + 32.0;
temp=celsius;
//====================
lcd.setCursor(0,1);
lcd.print("Temp:");
lcd.print(temp);
lcd.write(0xDF);
lcd.print("C ");
}
How it Works
1. Connect the Arduino with Peripherals needed.
2. Plug in the Power Source on the device.
3. Add some library if needed
4. Compile and upload the script program above to your arduino.5. On the LCD will display the temperature value read by Arduino with temperature sensor DS1820.
Video for Project II - 15. DS1820 (Waterproof Temperature Sensor) Monitoring with Arduino
Required file






No comments:
Post a Comment